[알고리즘] 6. 최단 경로
in 알고리즘
1. 최단 경로 (Shortest Path)
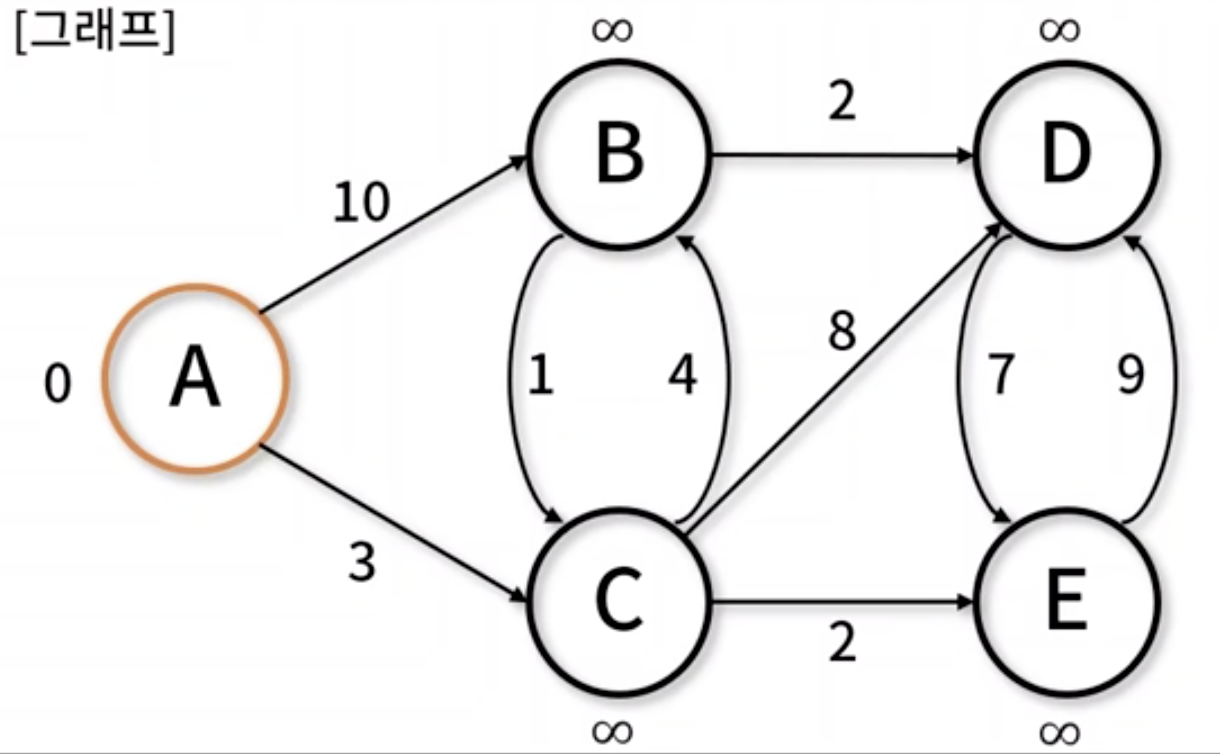
- 가중 그래프에서 구성하는 간선 간
가중치 합이 최소가 되도록 최단 경로를 찾는 알고리즘
최단 경로 알고리즘 유형
- Dijkstra 알고리즘 : 단일 최단 경로
최소 비용산출 - A* 알고리즘 :
휴리스틱 방법을 사용한 탐색 - Bellman-Ford 알고리즘 :
음수 가중치를 허용한 비용 산출 - Floyd-Warshall 알고리즘 :
동적 계획법기반의 고차원 기법
2. Dijkstra 알고리즘
- 그래프에서
출발점과 도착점 사이의 최단 거리를 구하는 알고리즘 - 보통 단일 정점 간 최단 경로 산출 시 사용, 도로 교통 망이나 OSPF 등의 네트워크 라우팅 프로토콜에 널리 이용
- 정점 / 간선 추가 :
ShortestPath.addVertex(),ShortestPath.addEdge() - 다익스트라 알고리즘 :
ShortestPath._extractMin(),ShortestPath.dijkstra()
3. Dijkstra 구현하기
// ShortestPath() : edge object 객체 저장을 위한 생성자
// key : vertex
// value : list 형태로 연결된 vertex를 표현하여 edge 연결 관계 표현
function ShortestPath() {
this.edges = {};
}
// addVertex() : 정점 추가 (간선 비용 표시를 위해 key/value object 형태로 저장)
ShortestPath.prototype.addVertex = function (vertex) {
this.edges[vertex] = {};
};
// addEdge() : 간선추가
ShortestPath.prototype.addEdge = function (srcVertex, dstVertex, weight) {
this.edges[srcVertex][dstVertex] = weight;
};
// _extractMin() : 최단 거리 노드 검색
ShortestPath.prototype._extractMin = function (queue, dist) {
let minDistance = Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
let minVertex = null;
for (let vertex in queue) {
if (dist[vertex] <= minDistance) {
minDistance = dist[vertex];
minVertex = vertex;
}
}
return minVertex;
};
// dijkstra() : 다익스트라 최단 경로 탐색
ShortestPath.prototype.dijkstra = function (start) {
let queue = {};
let dist = {};
for (let vertex in this.edges) {
dist[vertex] = Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
queue[vertex] = this.edges[vertex];
}
dist[start] = 0;
while (Object.keys(queue).length != 0) {
let u = this._extractMin(queue, dist);
delete queue[u];
for (let neighbor in this.edges[u]) {
let alt = dist[u] + this.edges[u][neighbor];
if (alt < dist[neighbor]) dist[neighbor] = alt;
}
}
for (let vertex in this.edges) {
if (dist[vertex] === Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY) delete dist[vertex];
}
return dist;
};
let path = new ShortestPath();
path.addVertex("A");
path.addVertex("B");
path.addVertex("C");
path.addVertex("D");
path.addVertex("E");
path.addEdge("A", "B", 10);
path.addEdge("A", "C", 3);
path.addEdge("B", "C", 1);
path.addEdge("B", "D", 2);
path.addEdge("C", "B", 4);
path.addEdge("C", "D", 8);
path.addEdge("C", "E", 2);
path.addEdge("D", "E", 7);
path.addEdge("E", "D", 9);
console.log(path);
// ShortestPath {
// edges: {
// A: { B: 10, C: 3 },
// B: { C: 1, D: 2 },
// C: { B: 4, D: 8, E: 2 },
// D: { E: 7 },
// E: { D: 9 }
// }
// }
console.log(path.dijkstra("A"));
// { A: 0, B: 7, C: 3, D: 9, E: 5 }
5. Floyd-Warshall 알고리즘
동적 계획법을 활용해, 그래프에서가능한 모든 정점 쌍에 대해 최단 거리를 구하는 알고리즘- 음의 가중치가 있어도 사용 가능하며, 많은 수의 간선으로 이루어져 있는 밀집 그래프(Dense Graph)에 사용 적합
- 정점/간선 추가 :
ShortestPath.addVertex(),ShortextPath.addEdge() - 플로이드-워셜 알고리즘 :
ShortestPath.floydWarshall()
6. Floyd-Warshall 구현하기
ShortestPath.prototype.floydWarshall = function () {
let dist = {};
for (let srcVertex in this.edges) {
dist[srcVertex] = {};
for (let dstVertex in this.edges) {
if (srcVertex === dstVertex) dist[srcVertex][dstVertex] = 0;
else dist[srcVertex][dstVertex] = Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
}
}
for (let srcVertex in this.edges) {
for (let dstVertex in this.edges[srcVertex]) {
dist[srcVertex][dstVertex] = this.edges[srcVertex][dstVertex];
}
}
for (let minVertex in this.edges) {
for (let srcVertex in this.edges) {
for (let dstVertex in this.edges) {
dist[srcVertex][dstVertex] = Math.min(
dist[srcVertex][dstVertex],
dist[srcVertex][minVertex] + dist[minVertex][dstVertex]
);
}
}
}
for (let srcVertex in this.edges) {
for (let dstVertex in this.edges) {
if (dist[srcVertex][dstVertex] === Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY)
delete dist[srcVertex][dstVertex];
}
}
return dist;
};
let path = new ShortestPath();
path.addVertex("A");
path.addVertex("B");
path.addVertex("C");
path.addVertex("D");
path.addVertex("E");
path.addEdge("A", "B", 10);
path.addEdge("A", "C", 3);
path.addEdge("B", "C", 1);
path.addEdge("B", "D", 2);
path.addEdge("C", "B", 4);
path.addEdge("C", "D", 8);
path.addEdge("C", "E", 2);
path.addEdge("D", "E", 7);
path.addEdge("E", "D", 9);
console.log(path);
// ShortestPath {
// edges: {
// A: { B: 10, C: 3 },
// B: { C: 1, D: 2 },
// C: { B: 4, D: 8, E: 2 },
// D: { E: 7 },
// E: { D: 9 }
// }
// }
console.log(path.dijkstra("A"));
console.log(path.dijkstra("B"));
console.log(path.dijkstra("C"));
console.log(path.dijkstra("D"));
console.log(path.dijkstra("E"));
// { A: 0, B: 7, C: 3, D: 9, E: 5 }
// { B: 0, C: 1, D: 2, E: 3 }
// { B: 4, C: 0, D: 6, E: 2 }
// { D: 0, E: 7 }
// { D: 9, E: 0 }
console.log(path.floydWarshall());
// {
// A: { A: 0, B: 7, C: 3, D: 9, E: 5 },
// B: { B: 0, C: 1, D: 2, E: 3 },
// C: { B: 4, C: 0, D: 6, E: 2 },
// D: { D: 0, E: 7 },
// E: { D: 9, E: 0 }
// }
