[알고리즘] 5. 동적 계획법
in 알고리즘
1. 동적 계획법 (Dynamic programming)
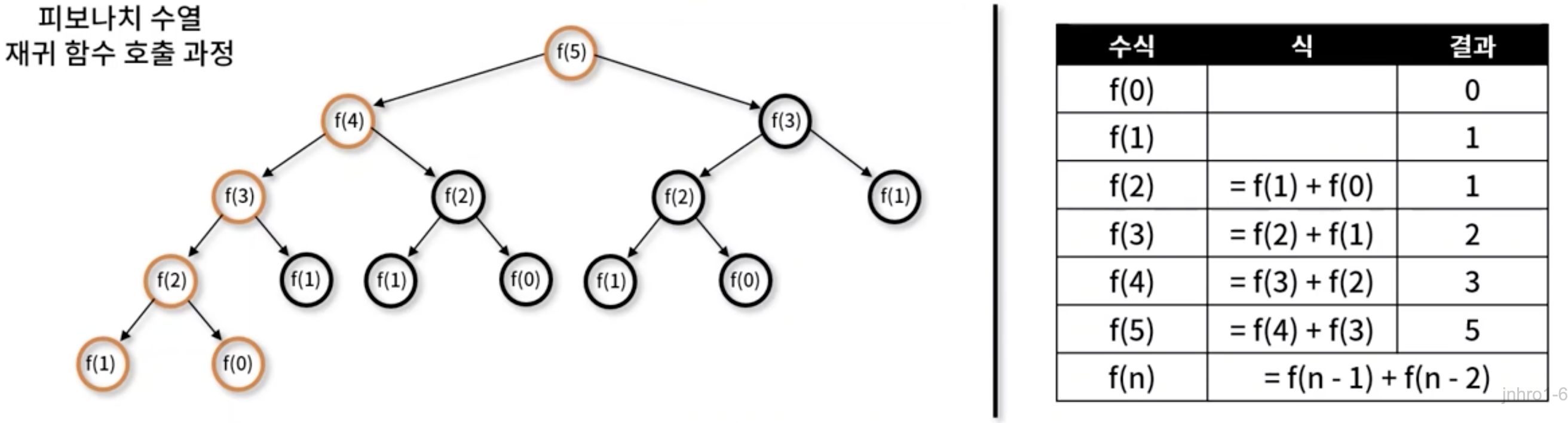
Memorization으로 중복 연산을 방지하며,작은 부분 문제로 큰 문제를 해결하며 해를 도출하는 알고리즘 설계 기법부문 문제는 중복되며,상위 문제 해결 시 재사용- Memoriaion 기법을 사용 (동일한 계산을 반복할 때, 이전에 계산한 값을 메모리에 저장하여 중복 연산 방지)
- 점화식을 기본으로 코드를 작성한다.
동적 계획법 구현 방석
- Top-down : 재귀를 통해 큰 문제를 작은 문제로 나눠 해결하며 해를 찾는 방법
function fibo_td(n, d = []){
if (n<2) return n
if (d[n]) return d[n]
d[n] = fibo_td(n-1) + fibo_td(n-2)
return d[n]
}
console.log(fibo_td(5)) //5
console.log(fibo_td(6)) //8
console.log(fibo_td(7)) //13
- Bottom-up : 반복문을 통해 작은 문제부터 차례대로 해를 찾는 방법
function fibo_bu(n, d = []){
d[0] = 0
d[1] = 1
for (let i =2; i<=n; i++){
d[i] = d[i-1] + d[i-2]
}
return d[n]
}
console.log(fibo_bu(5)) //5
console.log(fibo_bu(6)) //8
console.log(fibo_bu(7)) //13
2. 문제 - 거스름돈🤔
function solution(n, money) {
let dp = new Array(n + 1).fill(0);
dp[0] = 1;
for (let coin of money) {
for (let price = coin; price <= n; price++) {
dp[price] += dp[price - coin];
}
}
return dp[n] % 1000000007;
}
3. 정수 삼각형🤔
function solution(triangle) {
let answer = 0;
let height = triangle.length;
let d = Array(501)
.fill(0)
.map(() => Array(501).fill(0));
answer = d[0][0] = triangle[0][0];
for (let i = 1; i < height; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
if (j == 0) {
d[i][j] = d[i - 1][j] + triangle[i][j];
console.log(d[i][j]);
} else if (j == i) {
d[i][j] = d[i - 1][j - 1] + triangle[i][j];
console.log(d[i][j]);
} else {
d[i][j] = Math.max(d[i - 1][j - 1], d[i - 1][j]) + triangle[i][j];
}
answer = Math.max(answer, d[i][j]);
}
}
return answer;
}
const tc = [[7], [3, 8], [8, 1, 0], [2, 7, 4, 4], [4, 5, 2, 6, 5]];
console.log(solution(tc)); //30
