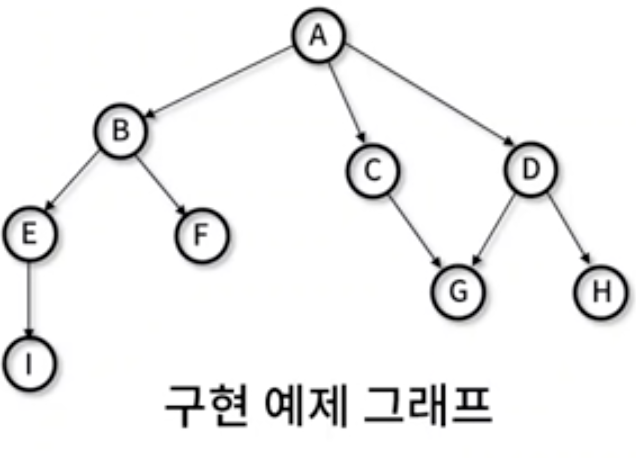
// _bfsShortesPath() : 다른 정점 간 최단 경로 비용 산출
Graph.prototype._bfsShortesPath = function (vertex) {
let queue = new Queue();
queue.enqueue(vertex);
let distance = {};
let pre_visit = {};
for (let vertex in this.edge) {
distance[vertex] = 0;
pre_visit[vertex] = null;
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
let vertex = queue.deuqeue();
this.visited[vertex] = true;
console.log(`visit "${vertex}"`);
let neighbors = this.edge[vertex];
for (let i = 0; i < neighbors.length; i++) {
if (!this.visited[neighbors[i]]) {
distance[neighbors[i]] = distance[vertex] + 1;
pre_visit[neighbors[i]] = vertex;
queue.enqueue(neighbors[i]);
}
}
}
return { distance, pre_visit };
};
// _from_to_path() : from 정점에서 to 정점으로 최단 경로 출력
Graph.prototype._from_to_path = function (pre_visit, from, to) {
let stack = new Stack();
for (let v = to; v !== from; v = pre_visit[v]) {
stack.push(v);
}
stack.push(from);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
let v = stack.pop();
process.stdout.write(`${v} -> `);
}
console.log("end");
};
// shortestPath() : 다른 정점 간 최단 경로 탐색
Graph.prototype.shortestPath = function (startVertex) {
let result = this._bfsShortesPath(startVertex);
console.log(result.distance);
console.log(result.pre_visit);
for (let vertex in this.edge) {
if (vertex === startVertex) continue;
this._from_to_path(result.pre_visit, startVertex, vertex);
}
};
let q = new Queue();
console.log("q", q.isEmpty());
let graph = new Graph();
let vertices = ["A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", "G", "H", "I"];
for (let i = 0; i < vertices.length; i++) {
graph.addVertex(vertices[i]);
}
graph.addEdge("A", "B");
graph.addEdge("A", "C");
graph.addEdge("A", "D");
graph.addEdge("B", "E");
graph.addEdge("B", "F");
graph.addEdge("C", "G");
graph.addEdge("D", "G");
graph.addEdge("D", "H");
graph.addEdge("E", "I");
// graph.print();
// console.log("");
console.log(graph._bfsShortesPath("A"))
// {
// distance: { A: 0, B: 1, C: 1, D: 1, E: 2, F: 2, G: 2, H: 2, I: 3 },
// pre_visit: {
// A: null,
// B: 'A',
// C: 'A',
// D: 'A',
// E: 'B',
// F: 'B',
// G: 'D',
// H: 'D',
// I: 'E'
// }
// }
graph.shortestPath("A");
// visit "A"
// visit "B"
// visit "C"
// visit "D"
// visit "E"
// visit "F"
// visit "G"
// visit "G"
// visit "H"
// visit "I"
// { A: 0, B: 1, C: 1, D: 1, E: 2, F: 2, G: 2, H: 2, I: 3 }
// {
// A: null,
// B: 'A',
// C: 'A',
// D: 'A',
// E: 'B',
// F: 'B',
// G: 'D',
// H: 'D',
// I: 'E'
// }
// A -> B -> end
// A -> C -> end
// A -> D -> end
// A -> B -> E -> end
// A -> B -> F -> end
// A -> D -> G -> end
// A -> D -> H -> end
// A -> B -> E -> I -> end