[선형] 15. 해시테이블
1. 해시함수 (Hash Function)
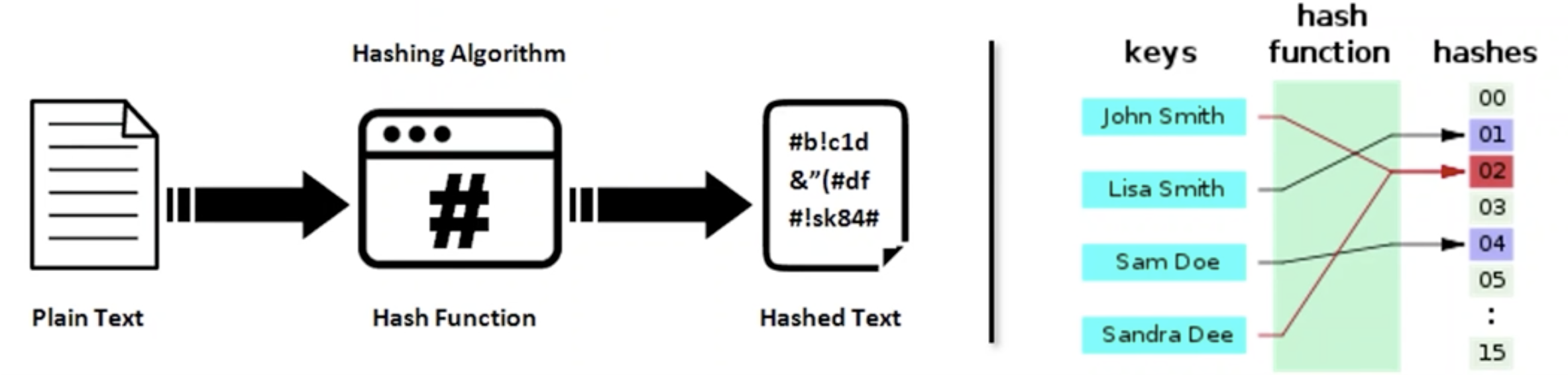
- 임의의 길이의 데이터를
고정된 길이의 데이터로 매핑하는 함수 - 압축성 : 다양한 가변 길이의 입력에 대해 고정된 크기의 결과값을 반환하는 성질
- 효율성 : 어떤 입력 값에 대해서도 많은 자원과 시간이 소요되지 않고 처리되는 성질
저항성: 결과값을 바탕으로 입력 값을 찾는 것이 불가능한 성질
2. 해시테이블 (Hash Table)
Hash 함수를 사용하여 평군 O(1) 시간 복잡도로 특정 값을 신속하게 찾는 자료구조- 충돌(Collision) 해결 방법
- 해시 함수 변경 : 더 큰 숫자의 공간과 Modular 산술 값을 이용해 충돌 최소화
- 자료구조 확장 : Open Addressing Method (선형 조사법, 이중해시), Close Addressing Method (체이닝)
- 객체 초기화 / 크기 반환 :
HashTable.clear(),HashTable.size() - 전체 데이터 반환, 전체 데이터 출력 :
HashTable.getBuffer(),HashTable.print() - 데이터 추가 / 삭제 / 반환 :
HashTable.put(),HashTable.remove(),HashTable.get()
3. 구현하기
생성자 HashTable(), hashCode()
// hash 는 자원이 한정적인 상황에서 성능을 최적화하는 가장 좋은 방법
const HASH_SIZE = 37;
// Element() : key, value 저장을 위한 생성자
function Element(key, value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
// HashTable() : 생성자
function HashTable() {
this.table = new Array(HASH_SIZE);
this.length = 0;
}
// hashCode() : 해시 함수
HashTable.prototype.hashCode = function (key) {
let hash = 0;
// loselosehash
for (let i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {
hash += key.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % HASH_SIZE;
};
let ht = new HashTable();
console.log(ht); //HashTable { table: [ <37 empty items> ], length: 0 }
console.log(ht.hashCode("Jo")); //0
console.log(ht.hashCode("Na")); //27
console.log(ht.hashCode("Hyun")); //13
put(), get(), remove()
// put() : 데이터 추가
HashTable.prototype.put = function (key, value) {
let index = this.hashCode(key);
console.log(`key: ${key} -> index: ${index}`);
// 해시테이블 충돌 나는 것 > 해결해야한다!
if (this.table[index] !== undefined) {
return false;
}
this.table[index] = new Element(key, value);
this.length++;
return true;
};
// get() : 데이터 조회
HashTable.prototype.get = function (key) {
return this.table[this.hashCode(key)];
};
// remove() : 데이터 삭제
HashTable.prototype.remove = function (key) {
let element = this.table[this.hashCode(key)];
if (element !== undefined) {
delete this.table[this.hashCode(key)];
this.length--;
}
return element;
};
let ht = new HashTable();
ht.put("Jo", 150);
ht.put("Na", 170);
ht.put("Hyun", 130);
// key: Jo -> index: 0
// key: Na -> index: 27
// key: Hyun -> index: 13
console.log(ht);
// HashTable {
// table: [
// Element { key: 'Jo', value: 150 },
// <12 empty items>,
// Element { key: 'Hyun', value: 130 },
// <13 empty items>,
// Element { key: 'Na', value: 170 },
// <9 empty items>
// ],
// length: 3
// }
console.log(ht.get("Jo")); //Element { key: 'Jo', value: 150 }
console.log(ht.remove("Jo")); //Element { key: 'Jo', value: 150 }
console.log(ht.get("Jo")); //undefined
console.log(ht.remove("Na")); //Element { key: 'Na', value: 170 }
console.log(ht);
// HashTable {
// table: [
// <13 empty items>,
// Element { key: 'Hyun', value: 130 },
// <23 empty items>
// ],
// length: 1
// }
clear(), size(), getBuffer(), print()
// clear() : 초기화
HashTable.prototype.clear = function () {
this.table = new Array(HASH_SIZE);
this.length = 0;
};
// size() : 크기 변환
HashTable.prototype.size = function () {
return this.length;
};
// getBuffer() : 데이터 셋 반환
HashTable.prototype.getBuffer = function () {
let array = [];
for (let i = 0; i < this.table.length; i++) {
if (this.table[i]) {
array.push(this.table[i]);
}
}
return array;
};
// print() : 데이터 셋 출력
HashTable.prototype.print = function () {
for (let i = 0; i < this.table.length; i++) {
if (this.table[i]) {
console.log(`${i} -> ${this.table[i].key} : ${this.table[i].value}`);
}
}
};
let ht = new HashTable();
ht.put("Jo", 150);
ht.put("Na", 170);
ht.put("Hyun", 130);
ht.print()
// 0 -> Jo : 150
// 13 -> Hyun : 130
// 27 -> Na : 170
console.log(ht.getBuffer())
// [
// Element { key: 'Jo', value: 150 },
// Element { key: 'Hyun', value: 130 },
// Element { key: 'Na', value: 170 }
// ]
console.log(ht.size()) //3
ht.clear()
console.log(ht) //HashTable { table: [ <37 empty items> ], length: 0 }
4. 해시테이블 충돌 및 해결
기존 코드 충돌 문제 (use loselose)
let ht = new HashTable();
ht.put("Ana", 150);
ht.put("Donnie", 170);
ht.put("Sue", 130);
ht.put("Jamie", 140);
ht.put("Paul", 200);
// key: Ana -> index: 13
// key: Donnie -> index: 13
// key: Sue -> index: 5
// key: Jamie -> index: 5
// key: Paul -> index: 32
console.log(ht)
// HashTable {
// table: [
// <5 empty items>,
// Element { key: 'Sue', value: 130 },
// <7 empty items>,
// Element { key: 'Ana', value: 150 },
// <18 empty items>,
// Element { key: 'Paul', value: 200 },
// <4 empty items>
// ],
// length: 3
// }
console.log(ht.size()) //3
충돌 해결 (use djb2)
const HASH_SIZE = 1013;
// djb2 hash function
HashTable.prototype.hashCode = function (key) {
let hash = 5831; //seed
// loselosehash
for (let i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {
hash += hash * 33 + key.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % HASH_SIZE;
};
let ht = new HashTable();
ht.put("Ana", 150);
ht.put("Donnie", 170);
ht.put("Sue", 130);
ht.put("Jamie", 140);
ht.put("Paul", 200);
// key: Ana -> index: 467
// key: Donnie -> index: 182
// key: Sue -> index: 244
// key: Jamie -> index: 533
// key: Paul -> index: 619
console.log(ht);
// HashTable {
// table: [
// <182 empty items>,
// Element { key: 'Donnie', value: 170 },
// <61 empty items>,
// Element { key: 'Sue', value: 130 },
// <222 empty items>,
// Element { key: 'Ana', value: 150 },
// <65 empty items>,
// Element { key: 'Jamie', value: 140 },
// <85 empty items>,
// Element { key: 'Paul', value: 200 },
// <393 empty items>
// ],
// length: 5
// }
5. 문제 - 숫자 카드
카드 게임을 하기 위해 -10 ~ 10 사이의 숫자 카드를 N장 뽑았다.
이 때 M개 수가 갖는 숫자 카드가 몇 개 있는지 계산해주는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
숫자 카드 범위는 -10 <= 카드 <= 10 이며, N 과 M의 범위는 3 <= N, M <= 20 이다.
입력은 숫자 카드 범위를 만족하는 N과 M 배열이 순차적으로 들어오며, M 숫자 카드를 몇 개 갖고 있는지를 순차적으로 배열이 기록하며 반환한다.
const HASH_SIZE = 21;
function HashTable() {
this.table = new Array(HASH_SIZE);
}
HashTable.prototype.hashCode = function (key) {
return (key + 10) % HASH_SIZE; // -10 ~ 10 > 0 ~ 20
};
HashTable.prototype.put = function (key) {
let index = this.hashCode(key);
if (this.table[index] === undefined) {
this.table[index] = 0;
}
this.table[index]++;
};
HashTable.prototype.get = function (key) {
return this.table[this.hashCode(key)] === undefined
? 0
: this.table[this.hashCode(key)];
};
function answer(card, select) {
let result = [];
// 구현
let hash = new HashTable();
// 1. card 내 있는 숫자 카드가 몇개인지를 count
for (let i = 0; i < card.length; i++) {
hash.put(card[i]);
}
// 2. select 내 있는 숫자 카드가 1번의 count 한 배열에서 몇 개 있는지 확인
for (let i = 0; i < select.length; i++) {
result.push(hash.get(select[i]));
}
// 구현 종료
return result;
}
let input = [
// TC : 1
[
[-6, -1, 6, 1, 1],
[-2, 1, 3],
],
[
[7, 4, 3, 10, 10, 10, -10, -10, 7, 3],
[10, 9, -5, 4, 6, -10],
],
[
[5, -3, -7, 10, -3, 4, 8, 4, -3, 3, 8, -2, -9, -8, -1],
[4, 5, 1, 10, -2, -3, 3, -8],
],
];
for (let i = 0; i < input.length; i++) {
process.stdout.write(`#${i + 1}`);
console.log(answer(input[i][0], input[i][1]));
}
// #1[ 0, 2, 0 ]
// #2[ 3, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2 ]
// #3[
// 2, 1, 0, 1,
// 1, 3, 1, 1
// ]
