[선형] 6. 연결리스트
1. 연결 리스트 (Linked list)
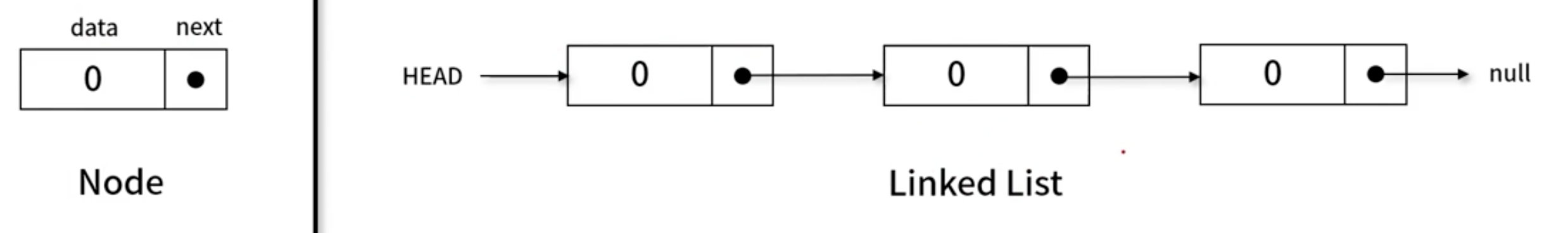
- 각 노드가 데이터와 포인터를 가지며,
한 줄로 연결되어 있는 방식으로 데이터를 저장하는 자료 구조 - Node : data + next(pointer)
- Linked List = HEAD + NODE
- 노드 개수 / 비어있는지 확인 / 노드 출력 :
LinkedList.size(),LinkedList.isEmpty(),LinkedList.printNode() - 노드 추가 :
LinkedList.append(),LinkedList.insert() - 노드 삭제 :
LinkedList.remove(),LinkedList.removeAt() - 데이터 위치 확인 :
LinkedList.indexOf()
2. 연결 리스트 구현하기
1. 구현
// Node() : data와 point를 가지고 있는 객체
function Node(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
// LinkedList() : head와 length를 가지고 있는 객체
function LinkedList() {
this.head = null;
this.length = 0;
}
// size() : 연결 리스트 내 노드 개수 확인
LinkedList.prototype.size = function () {
return this.length;
};
// imEmpty() : 객체 내 노드 존재 여부 파악
LinkedList.prototype.isEmpty = function () {
return this.length === 0;
};
let ll = new LinkedList();
console.log(ll); //LinkedList { head: null, length: 0 }
ll.head = new Node(123);
ll.length++;
console.log(ll); //LinkedList { head: Node { data: 123, next: null }, length: 1 }
ll.head.next = new Node(456);
ll.length++;
console.log(ll);
// LinkedList {
// head: Node { data: 123, next: Node { data: 456, next: null } },
// length: 2
// }
2. printNode(), append()
// printNode : 노드 출력
LinkedList.prototype.printNode = function (){
for (let node = this.head; node != null; node = node.next){
process.stdout.write(`${node.data} -> `)
}
console.log(null)
}
// append() : 연결 리스트 가장 끝에 노드 추가
LinkedList.prototype.append = function (value) {
let node = new Node(value)
let current = this.head
if (this.head === null){
this.head = node
} else {
while(current.next != null){
current = current.next
}
current.next = node
}
this.length++
}
ll.append(1)
ll.append(13)
ll.append(199)
ll.printNode() //123 -> 456 -> 1 -> 13 -> 199 -> null
console.log(ll.size()) // 5
3. insert()
// insert() : position 위치에 노드 추가
LinkedList.prototype.insert = function (value, position = 0) {
if (position < 0 || position > this.length){
return false;
}
let node = new Node(value),
current = this.head,
index = 0,
prev;
if (position === 0){
node.next = current;
this.head = node
} else {
while (index++ < position){
prev = current;
current = current.next;
}
node.next = current
prev.next = node
}
this.length++
return true
}
let ll2 = new LinkedList()
ll2.insert(1)
ll2.insert(10)
ll2.insert(100)
ll2.insert(2,1)
ll2.printNode() //100 -> 2 -> 10 -> 1 -> null
console.log(ll2.size()) //4
4. remove()
// remove() : value 데이터를 찾아 노드 삭제
LinkedList.prototype.remove = function (value) {
let current = this.head,
prev = current;
while (current.data != value && current.next != null) {
prev = current;
current = current.next;
}
if (current.data != value) {
return null;
}
if (current === this.head) {
this.head = current.next;
} else {
prev.next = current.next;
}
this.length--;
return current.data;
};
let ll = new LinkedList();
ll.insert(1);
ll.insert(10);
ll.insert(100);
ll.insert(2, 1);
ll.insert(3, 3);
ll.printNode(); //100 -> 2 -> 10 -> 3 -> 1 -> null
console.log(ll.size()); //5
console.log(ll.remove(1000))
ll.printNode(); //null
console.log(ll.remove(1))
ll.printNode(); //100 -> 2 -> 10 -> 3 -> null
console.log(ll.remove(2))
ll.printNode(); //100 -> 10 -> 3 -> null
console.log(ll.remove(100))
ll.printNode(); //10 -> 3 -> null
console.log(ll.size()); //2
5. removeAt()
// removeAt() : position 위치 노드 삭제
LinkedList.prototype.removeAt = function (position = 0) {
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length){
return null
}
let current = this.head,
index = 0,
prev;
if (position === 0){
this.head = current.next
} else {
while(index++ < position){
prev = current;
current = current.next
}
prev.next = current.next
}
this.length--
return current.data
};
let ll = new LinkedList();
ll.insert(1);
ll.insert(10);
ll.insert(100);
ll.insert(2, 1);
ll.insert(3, 3);
ll.printNode(); //100 -> 2 -> 10 -> 3 -> 1 -> null
console.log(ll.size()); //5
console.log(ll.removeAt(1000))
ll.printNode(); //null
console.log(ll.removeAt(4)) //1
ll.printNode(); //100 -> 2 -> 10 -> 3 -> null
console.log(ll.removeAt()) //100
ll.printNode(); //2 -> 10 -> 3 -> null
console.log(ll.removeAt(1)) //10
ll.printNode(); //2 -> 3 -> null
console.log(ll.size()); //2
6. indexOf()
// indexOf() : value 값을 갖는 노드 위치 반환
LinkedList.prototype.indexOf = function (value) {
let currnet = this.head,
index = 0;
while (current != null) {
if (current.data === value) {
return index;
}
index++;
current = currnet.next;
}
return -1;
};
// remove2() : indexOf + removeAt = remove
LinkedList.prototype.remove2 = function (value) {
let index = this.indexOf(value);
return this.removeAt(index);
};
let ll = new LinkedList();
ll.insert(1);
ll.insert(10);
ll.insert(100);
ll.insert(2, 1);
ll.insert(3, 3);
ll.printNode(); //100 -> 2 -> 10 -> 3 -> 1 -> null
console.log(ll.size()); //5
console.log(ll.indexOf(1000)); //-1
console.log(ll.indexOf(1));
console.log(ll.indexOf(100));
console.log(ll.indexOf(10));
console.log(ll.size());
console.log(ll.remove2(1000));
ll.printNode(); //null
console.log(ll.remove2(1)); //1
ll.printNode(); //100 -> 2 -> 10 -> 3 -> null
console.log(ll.removremove2eAt(2)); //100
ll.printNode(); //2 -> 10 -> 3 -> null
console.log(ll.remove2(100)); //10
ll.printNode(); //2 -> 3 -> null
console.log(ll.size()); //2
내가 스스로 짤 수 있을 때까지 완벽하게 이해하고 복습하기!
3. 열차 연결
새로운 지하철 노선이 신설되어, 이를 위한 열차가 새로 반입되었다.
하지만 이 열차들은 서로 연결되어 있지 않아 현재 운행이 어려운 상태이다.
열차 운행을 위해 열차 찻간을 이어주는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
열차 별로 고유의 식별번호가 있어, 이를 기준으로 반입된 순서대로 열차 찻간을 이어주도록 한다.
입력은 배열 형태로 열차 식별번호가 주어지며, 열차 찻간을 이어주어 Linked List 형태로 반환한다.
열차 연결 및 반환을 위해 사용해야 할 Train 객체와 Linked List 객체는 템플릿 코드를 참고한다.
function Train(number) {
this.number = number;
this.next = null;
}
function LinkedList() {
this.head = null;
}
function answer(nums) {
let ll = new LinkedList();
// 코드 구현 시작 영역
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
let train = new Train(nums[i]);
let current = ll.head;
if (ll.head === null) {
ll.head = train;
} else {
while (current.next != null) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = train;
}
}
// 코드 구현 종료 영역
return ll;
}
let input = [
[4, 7, 1, 10, 6],
[3, 10, 6, 9, 11, 3, 4],
[5, 8, 7, 3, 4, 1, 2, 7, 10, 7],
];
LinkedList.prototype.printNode = function () {
for (let node = this.head; node != null; node = node.next) {
process.stdout.write(`${node.number} -> `);
}
console.log("null");
};
for (let i = 0; i < input.length; i++) {
process.stdout.write(`#${i + 1}`);
answer(input[i]).printNode();
}
// #14 => 7 => 1 => 10 => 6 => null
// #23 => 10 => 6 => 9 => 11 => 3 => 4 => null
// #35 => 8 => 7 => 3 => 4 => 1 => 2 => 7 => 10 => 7 => null
// 시간복잡도 훨씬 줄어든다..!!
function answer(nums) {
let ll = new LinkedList();
// 코드 구현 시작 영역
let current, prev;
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
current = new Train(nums[i]);
if (i === 0) {
ll.head = current;
} else {
prev.next = current;
}
prev = current;
}
// 코드 구현 종료 영역
return ll;
}
4. 서류 정리
동생에게 전달해준 서류를 순서대로 서랍에 정리해달라고 부탁했더니, 서류를 반대 순서로 넣어두었다.
다시 서류를 정렬하기 위해, 이미 정리된 순서의 반대로 서류를 역 정렬시키는 프로그램을 제작하시오.
만약 서류가 1>2>3 순으로 들어가 있다면 3>2>1로 역 정렬시켜야 한다.
입력은 동생의 가공을 통해 역 정렬된 서류가 저장되어 있는 Linked list 객체가 주어지며,
포인트 조작을 통해 파일을 변경하여 Linked List 객체를 반환한다.
function File(number) {
this.number = number;
this.next = null;
}
function LinkedList() {
this.head = null;
}
function answer(ll) {
// 코드 구현 시작 영역
let data = []
for (let node = ll.head; node!=null; node = node.next){
data.push(node.number)
}
ll.head = null
ll.makeFiles(data)
// 코드 구현 종료 영역
return ll;
}
let input = [
[7,3,1],
[4,6,9,1,3],
[3,4,1,2,7,9,6],
];
LinkedList.prototype.printNode = function () {
for (let node = this.head; node != null; node = node.next) {
process.stdout.write(`${node.number} -> `);
}
console.log("null");
};
LinkedList.prototype.makeFiles = function (files) {
let current = this.head
let node;
for (let i = 0; i< files.length; i++){
node = new File(files[i])
node.next = current
this.head = node
current = node
}
}
for (let i = 0; i < input.length; i++) {
process.stdout.write(`#${i + 1}`);
let ll = new LinkedList()
ll.makeFiles(input[i])
answer(ll).printNode();
}
// #17 -> 3 -> 1 -> null
// #24 -> 6 -> 9 -> 1 -> 3 -> null
// #33 -> 4 -> 1 -> 2 -> 7 -> 9 -> 6 -> null
내 방법 너무 야매인가……….? 역방향 정렬 알아두기
function answer(ll) {
// 코드 구현 시작 영역
let current = ll.head,
prev = null,
next
// 1. 역방향 정렬
while (current != null){
next = current.next
current.next = prev
prev = current
current = next
}
// 2. head 업데이트
ll.head = prev
// 코드 구현 종료 영역
return ll;
}
